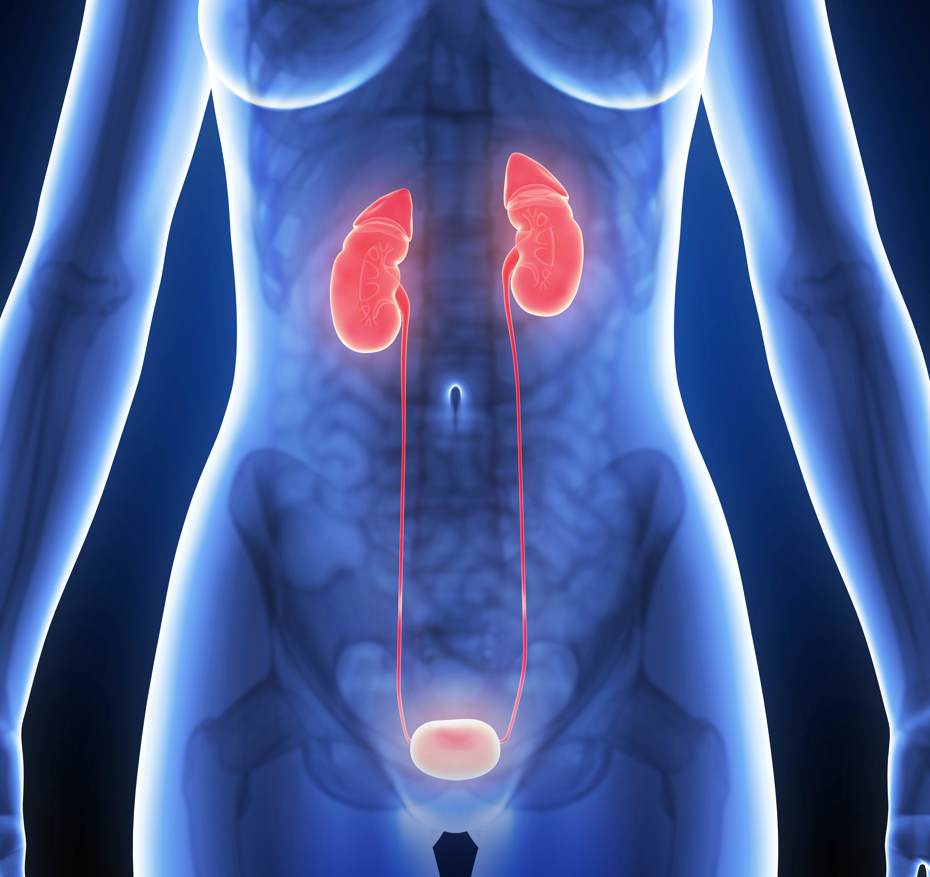
The Urinary System is responsible for the eliminating of waste and extra fluid in the body, by making and excreting urine.
It’s important that all parts of the urinary system work in partnership for normal urination to occur. The urinary system consists of kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra.
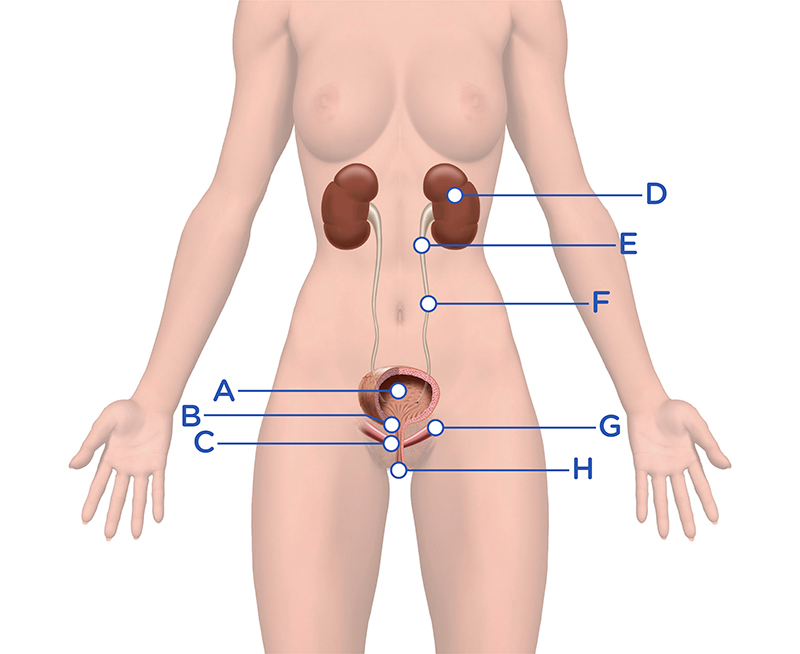
A = Bladder
B = Sphincter
D = Kidneys
E = Renal Pelvis
F = Ureter
G = Pelvic Floor Muscles
H = Urethra
The female anatomy consists of the urethra, approx 3-5 cm, which starts at the bottom of the bladder or bladder neck and extends downwards through the pelvic floor muscle, with the urethral orifice or external opening being situation between the clitoris and the vagina. For passive continence it is important that the mucous membrane in the urethra is elastic and well supplied with blood, for which the female hormone estrogen is responsible, and consists of a mixture of smooth and striated muscles.
When the woman enters menopause, estrogen production decreases, which affects the mucous membranes in the genital area and the urethra, causing it to become more fragile, dry and less elastic. Symptoms such as urine leakage, recurrent urinary tract infections and pain during intercourse are common.
Female Anatomy
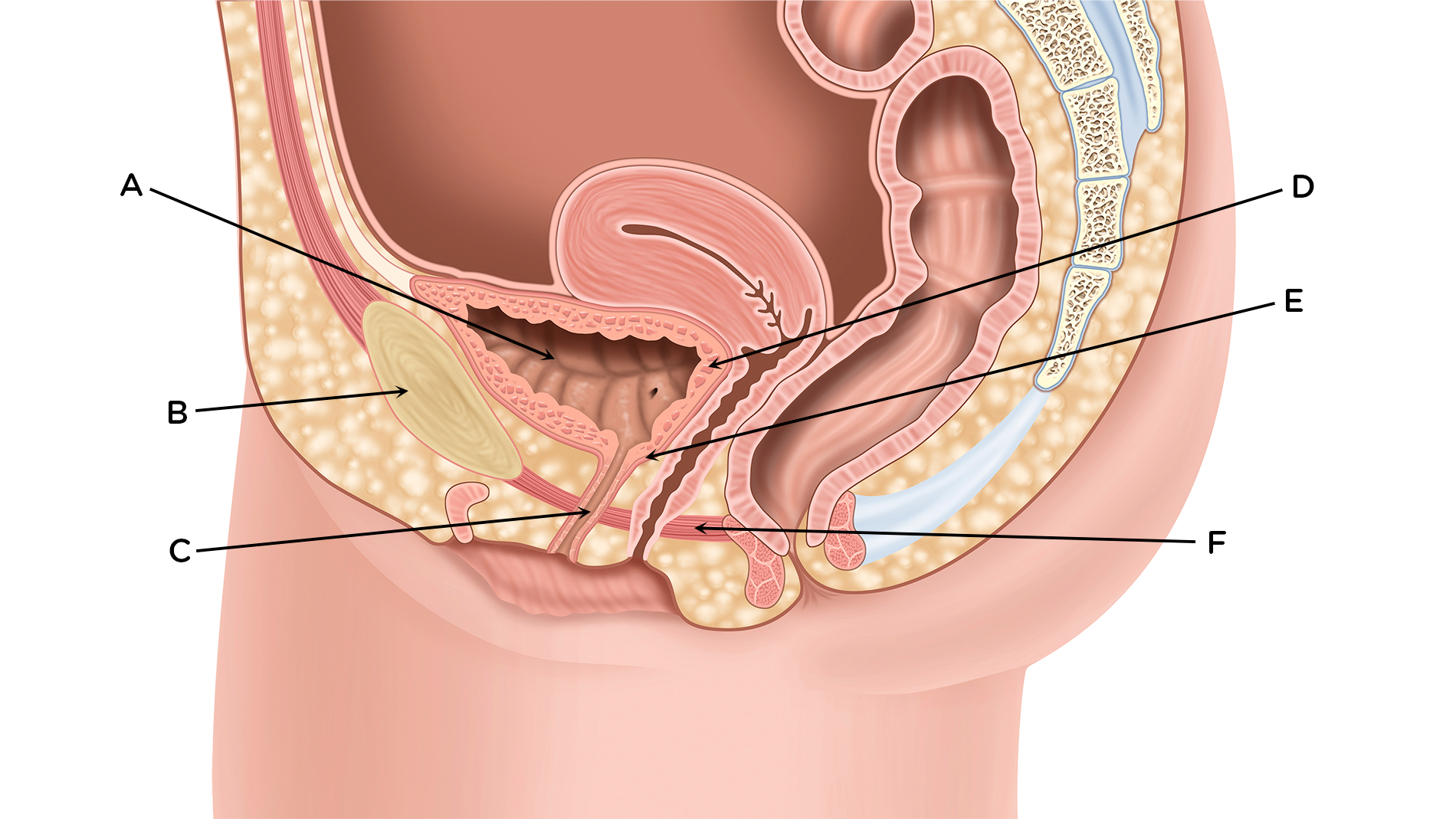
A = Bladder
B = Pelvic bone
C = Urethra
D = Detrusor muscle
E = Sphincter
F = Pelvic floor
Download the printable version below.