Course Theme: Bladder Not all catheters are the same
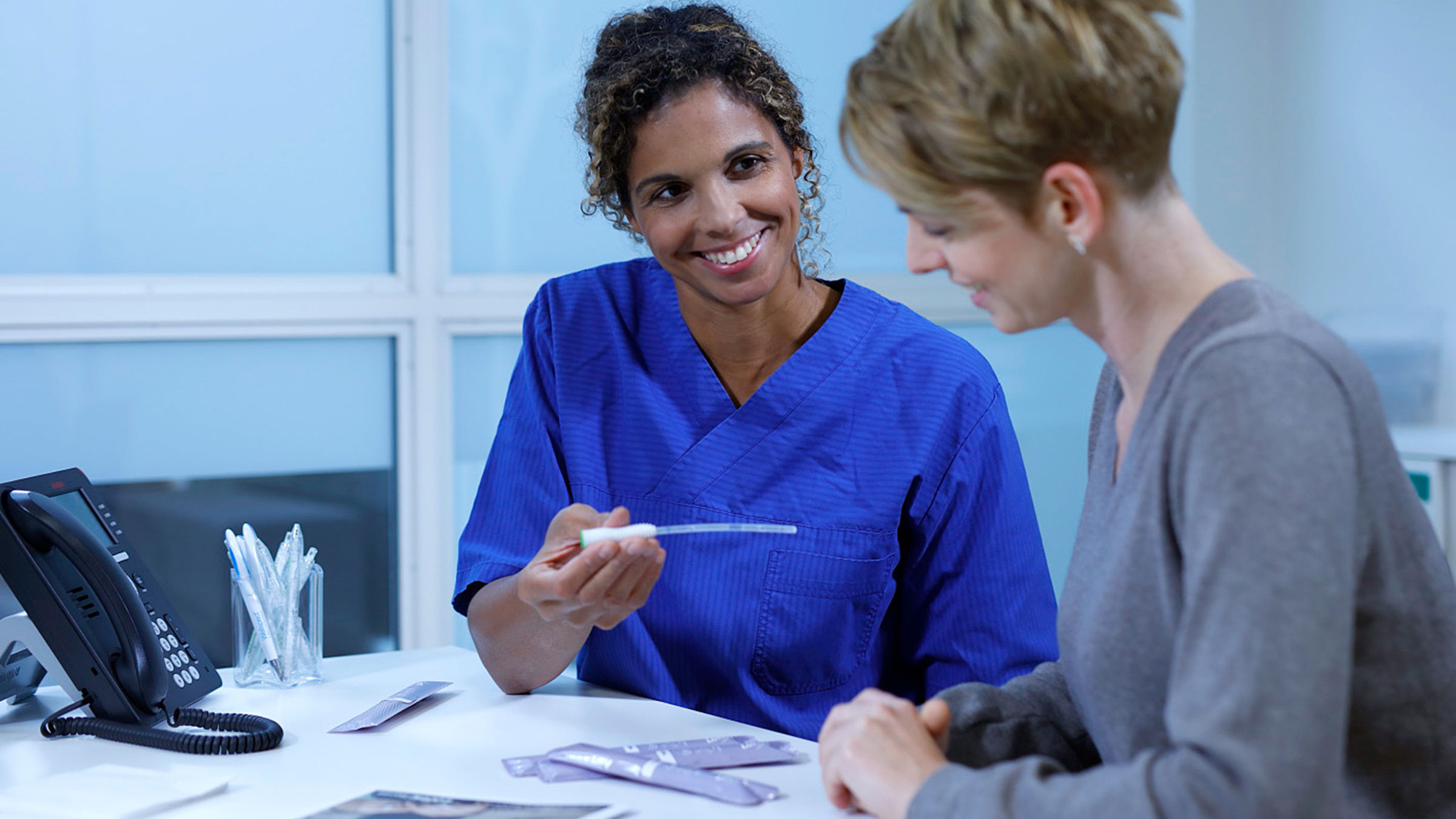
IC requires a high level of patient commitment, and some people may stop the therapy, particularly if under stress and other illness to deal with. Patients need to be well motivated and require an appropriate level of manual dexterity. Catheters with a surface osmolality in balance with urine is key to reducing friction during insertion and withdrawal. With more than 30 years on the market, LoFric has been shown to efficiently empty the bladder and reduce complications, such as hematuria and UTI, in the long-term.